Interface Paradigms
SYS 214 - Principles of HCI
agenda
Coming up on PHCI:
- Wednesday: Prototype Workshop!
- Bring your first prototype to class
- Be prepared to present it to the class and have someone try
- Nov 10: Prototype 1 Deliverable
Today: Interface Paradigms
- Describe the principle of cognitive metaphoric reasoning
- Use of prior knowledge to understand new situations
- Describe idiomatic design
project: next steps
Think about:
- What are the key objects and actions that the user needs to manipulate?
- What does your prototype need to convey?
interface paradigms
Implementation centric — UI is based upon the design of the app
- A UI piece is created to activate each created function
- Inner-workings are visible
- Focus: Technical knowledge
Metaphoric Interfaces
- Often visual
- Users connect visual cues and interface functions
- Focus: Intuitive Connections
Idiomatic Interfaces
- "Design of Principles"
- Focus: Quickly learned interactions
What is a metaphor?
- Metaphor
- A figure of speech in which a word or phrase that ordinarily designates one thing is used to designate another, thus making an implicit comparison, as in "a sea of troubles" or "All the world's a stage" (Shakespeare)
–The Free Dictionary
language use
Convey an abstract concept
Time is abstract
- We spend it
- We waste it
- We live on "borrowed time"
Exercise
- What are some metaphor terms that we use in interfaces?
- Think about:
- Actions we perform
- Objects on the screen
- Name of commands
- Think about:
- Can you find an example in a web site or an application?
Be prepared to share with the class.
Interface Metaphors
- Desktops
- Cutting
- Pasting
- Copying
- Trash
- Folder
Approach to New Technology
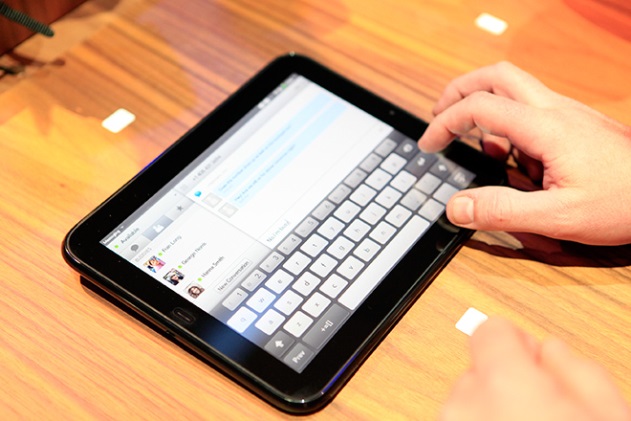


Behaves like a QWERTY Keyboard
- Spacebar
- Return Key
But there are differences
- Backspace and Spacebar
- Using a mouse for placement
Xerox Star System
|
 |

composite metaphors
|
Combining different metaphors together
|
 |
tablet metaphors
design principles
- Never bend your interface to fit a metaphor
- Avoid metaphors that do not clarify
- Avoid metaphors that clash
group discussion
Think about the metaphors you know and use.
What might be some challenges with using metaphors in design?
challenges
- Strict adherence
- Scale
- File icons
- Recognition across cultures
- Restrict thinking
- Often tied to the mechanical age
idioms
- Idioms
- A speech form or an expression of a given language that is peculiar to itself grammatically or cannot be understood from the individual meanings of its elements, as in keep tabs on or kick the bucket.
- Learned
- Many elements of the GUI
| · Windows | · Title bars |
| · Close boxes | · Hyperlinks |
| · Drop-downs | · Nested folders |
Cooper
“Idiomatic design is the future of interaction design.
”
—Alan Cooper
Cooper (GUI focused)
Idioms: Application specific commands and feedback
Compounds: Generic input and output actions and symbols
Primitives: Indivisible actions and feedback mechanisms
Cooper (GUI focused)
Primitives:
- Input
- Point
- Click
- Drag
- Keypress
- Output
- Cursor
- Text
Cooper (GUI focused)
Compounds:
- Input
- Button click
- Double-click
- Selection
- Output
- Edit fields
- Checkboxes
- Highlighting
Cooper (GUI focused)
Idioms:
- Input
- Delete
- Create
- Draw
- Output
- Scrolling
- Sorting
- Dialogs
Cooper (GUI focused)
“The familiar mouse is not metaphoric of anything but rather is learned idiomatically. That scene in Star Trek IV where Scotty returns to twentieth-century Earth and tries to speak into a mouse is one of the few parts of that movie that is not fiction. There is nothing about the mouse that indicates its purpose or use, nor is it comparable to anything else in our experience, so learning it is not intuitive. However, learning to point at things with a mouse is incredibly easy. Someone probably spent all of three seconds showing it to you your first time, and you mastered it from that instant on. We don't know or care how mice work and yet we can operate them just fine. That is idiomatic learning.
”
The Myth of Metaphor, by Alan Cooper, 1995. article
interface paradigms
Implementation centric — UI is based upon the design of the app
- A UI piece is created to activate each created function
- Inner-workings are visible
- Focus: Technical knowledge
Metaphoric Interfaces
- Often visual
- Users connect visual cues and interface functions
- Focus: Intuitive Connections
Idiomatic Interfaces
- "Design of Principles"
- Focus: Quickly learned interactions
