Gestalt Principles
SYS 214 - Principles of HCI
Agenda
- Project Notes
- Questions?
- START Researching
- Research update on Friday
- Assignment for Wed
- No additional assignment for Friday (RESEARCH!)
- DOET Principles from Friday
- DWMIM Principles for today
- Exercise
Causality
If something occurs after a user action, the user will assume causality.
Examples:
Causality
If something occurs after a user action, the user will assume causality.
Examples:
- I tried to print and the lights went off
- I click and something happens
Mapping
Takes advantage of physical and cultural analogies
Examples:
Mapping
Takes advantage of physical and cultural analogies
Examples:
- Car radio volume buttons
- Car steering wheel
- Light switches (on/off)
- Light switches (organization)
Visibility
Correct parts are visible and convey the right message.
Everything the user needs to complete the task is visible. Extra information is minimized.
Feedback
Status
- What has been done
- Where you are in a process
State changes
Result
What else?
"Leaving mark with a pencil"
Gestalt Principles
Gestalt Principles

- Proximity
- Similarity
- Continuity
- Closure
- Figure / Ground
- Common Fate
Gestalt Principles
What are these principles about?
Gestalt Principles
What are these principles about?
- They help us understand how our vision works.
- They enable us to create meaning through STRUCTURE!
- They enable us to quickly scan for the information we need.
Gestalt Principle: ???
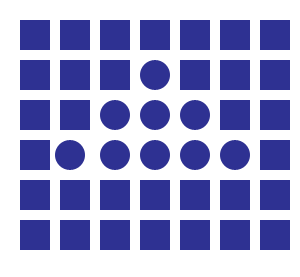
Gestalt Principle: Similarity

Notice how even though all of the shapes are the color that by changing the shape of the objects we also change how our minds group them together
Which seem related?
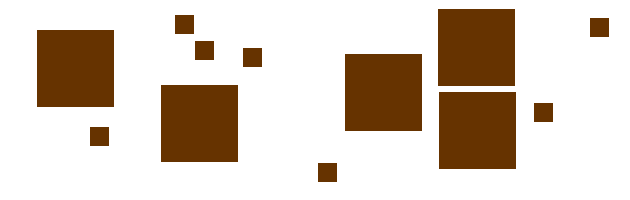
Which seem related?
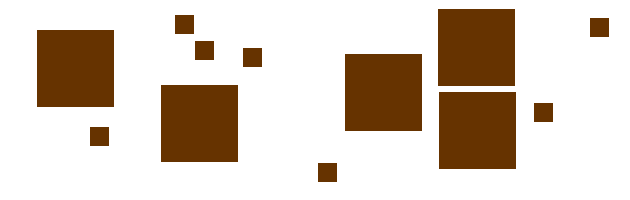
Shape, Color, Size
¬similarity
What's wrong with this picture?

similarity
Similar icons grouped

similarity
Blue/gray background to group icon to group
Gestalt principle: ???

Gestalt principle: closure

Our minds perceive items as a whole rather than separate pieces. In this case, a blank space is perceived as part of the form.
Gestalt principle: ???

Gestalt principle: Proximity

What's at play here?

What's at play here?

Proximity / Grouping
Proximity

Proximity

Common fate
Common fate

Drop downs that slide out together appear to be common fate.
gestalt principle: ???

gestalt principle: figure/ground

Figure and ground change as the focus of your eyes changes.
figure/ground
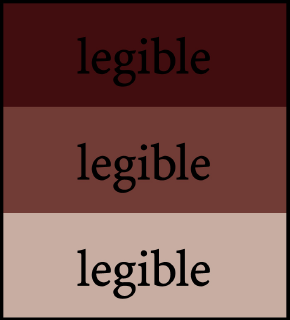
Figure/ground can impact legibility.
gestalt principle: ???
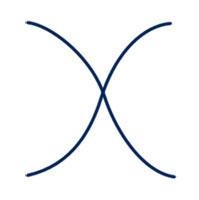
gestalt principle: continuity
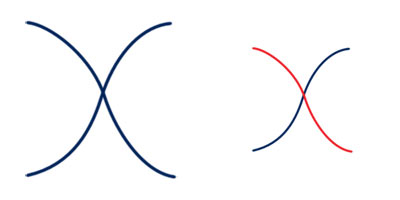
Continuity describes the tendency to see the left figure above as two curved lines. The right figure illustrates the two curved lines, one red and one blue.
Which seem related?

Hierarchy
What needs to be understood instantly?
Use hue, saturation, value, size, and position to distinguish hierarchy.

Hierarchy

exercise
Select a web site and find examples of some of these principles. Be prepared to share with the class.
- Proximity
- Similarity
- Continuity
- Closure
- Figure / Ground
- Common Fate
- Hierarchy
sources
http://sixrevisions.com/web_design/gestalt-principles-applied-in-design/
http://www.usask.ca/education/coursework/skaalid/theory/ gestalt/similar.htm
http://www.interaction-design.org/encyclopedia/gestalt_ principles_of_form_perception.html
http://andyrutledge.com/gestalt-principles-2-similarity.php
http://www.scientificjournals.org/journals2008/articles/1288.pdf
similarity

