Introduction to Course
COS 351 - Computer Vision
Who am I?
Professor:
- Dr. Jonathan Denning
- Ph.D. from Dartmouth College
- Computer Science
- focus: Computer Graphics
Disclaimer
These slides, for the most part, are not my own. The majority of this content was created by the James Hays, Derek Hoiem, Svetlana Lazebnik, and Steve Seitz.
Some info is a little old. Although I am working on updating the content and examples, the fundamentals and principles are the same.
Note: Computer Vision is a broad topic! We cannot cover everything :(
help!
Read the assigned book readings, so I can know if they were helpful.
learning
Syllabus
“Through this course, we will study the fundamental concepts of digital image acquisition, manipulation, enhancement, representation, analysis, and understanding.
”
Book

Required: Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications, 1st edition, Richard Szeliski, Springer, 2010. ISBN-13: 978-1-848-82934-3.
Important Note: use the electronic manuscript available by the author on the book's site http://szeliski.org/Book
Software
We will use a variety of software packages in this course.
- Matlab / Octave
- OpenCV (for Python)
- Blender
- Kinect SDK
- ...?
All of these are installed on the CSE lab machines and can be installed on your own machines.
prerequisites
Required:
- Course: COS 121
Not necessary, but extremely helpful
- Programming:
- experience with image processing
- Matlab programming
- Math:
- linear algebra
- basic calculus
- probability, statistics
computer vision
What is Computer Vision?
What are examples of computer vision being used in the world?
computer vision
Make computers understand images and video

- What kind of scene?
- Where are the cars?
- How far is the building?
- ...
computer vision
Vision is really hard
Vision is an amazing feat of natural intelligence
- Visual cortex occupies about 50% of a Macaque brain
- More human brain devoted to vision than anything else

computer vision
Why computer vision matters:




ridiculously brief history of cv

- 1966: Minsky assigns computer vision as an undergrad summer project
- 1960s: interpretation of synthetic worlds
- 1970s: some progress on interpreting selected images
- 1980s: ANNs come and go; shift toward geometry and increased mathematical rigor
- 1990s: face recognition; statistical analysis in vogue
ridiculously brief history of cv

- 2000s: broader recognition; large annotated datasets available; video processing starts
- 2010s: deep learning with ConvNets
- 2030s: robot uprising?
modern cv
The following is a short list of how vision is used today
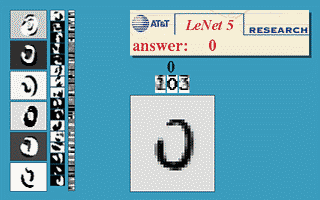
modern cv: optical character recognition
Technology to convert scanned docs to text
- if you have a scanner, it probably came with OCR software

modern cv: face detection
Many new digital cameras now detect faces
- Canon, Sony, Fuji, ...

modern cv: smile detection
“The Smile Shutter flow
”
Imagine a camera smart enough to catch every smile! In Smile Shutter Mode, your Cyber-shot® camera can automatically trip the shutter at just the right instant to catch the perfect expression.

modern cv: 3d from thousands of images
modern cv: vision-based biometrics

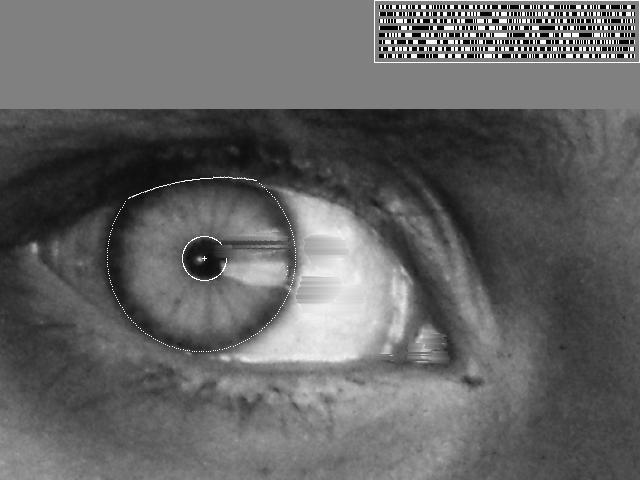
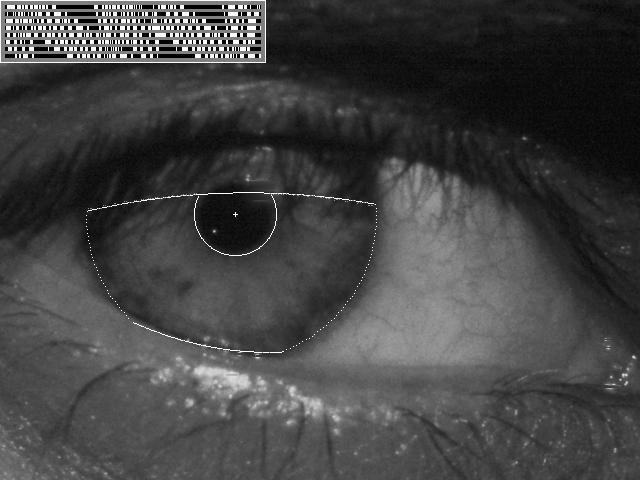
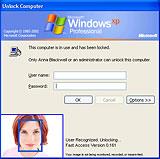
modern cv: login without a password
- Fingerprint scanners on many new laptops, other devices
- Face recognition systems now beginning to appear more widely


modern cv: recognition in supermarkets
“A smart camera is flush-mounted in the checkout lane, continuously watching for items. When an item is detected and recognized, the cashier verifies the quantity of items that were found under the basket, and continues to close the transaction. The item can remain under the basket, and with LaneHawk, you are assured to get paid for it...
”

modern cv: recognition in mobile phones
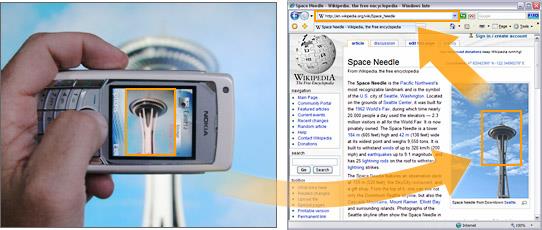
modern cv: recognition in mobile phones
modern cv: visual effects, shape capture
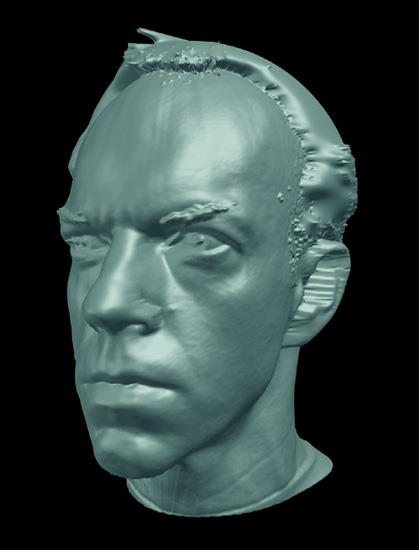


modern cv: visual effects, motion capture


modern cv: visual effects, motion capture
modern cv: sports
Sportvision visualizing first down line and other effects


modern cv: smart cars
- Vision systems currently in high-end BMW, GM, Volvo models
- By 2010: 70% of car manufacturers

modern cv: smart cars
modern cv: smart cars, google cars

- Oct 9, 2010. "Google Cars Drive Themselves, in Traffic". The New York Times. John Markoff.
- June 24, 2011. "Nevada state law paves the way for driverless cars". Financial Post. Christine Dobby.
- Aug 9, 2011. "Human error blamed after Google's driverless car sparks five-vehicle crash". The Star (Toronto).
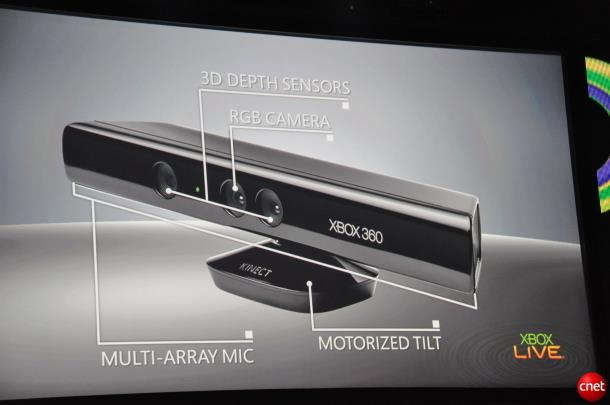
modern cv: interactive games, kinect

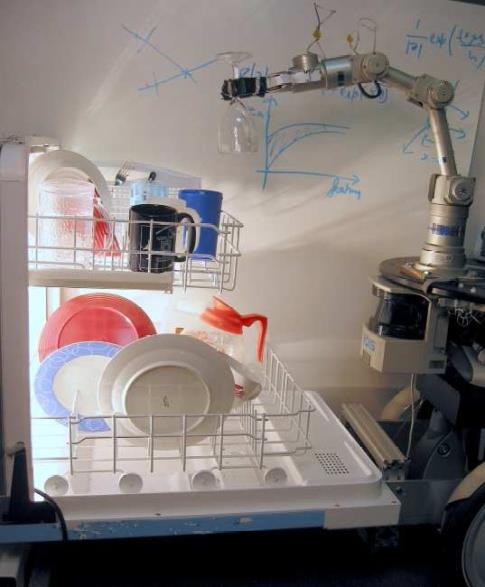
modern cv: industrial robots
Vision-guided robots position nut runners on wheels


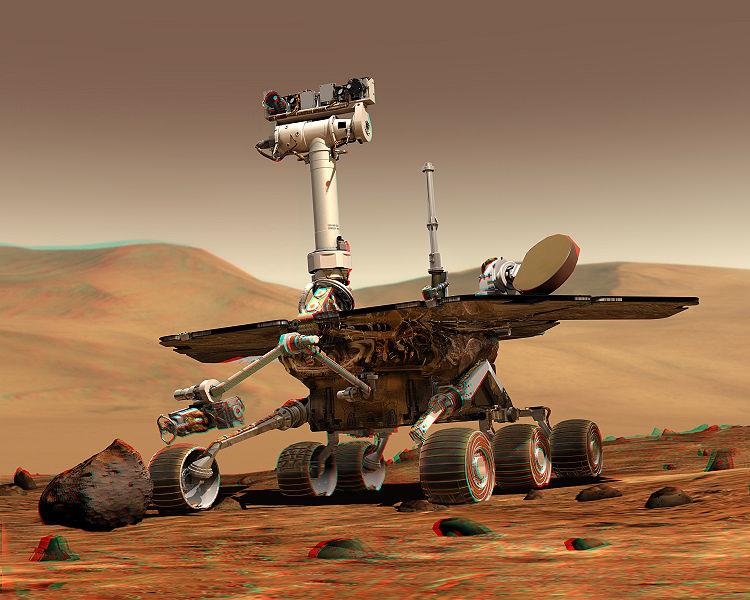
modern cv: vision in space

NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit captured this westward view from atop a low plateau where Spirit spent the closing months of 2007.
Vision Systems (JPL) used for several tasks: Panorama stitching, 3D terrain modeling, Obstacle detection, position tracking.
For more, read "Computer Vision on Mars" by Matthies et al.
modern cv: mobile robots


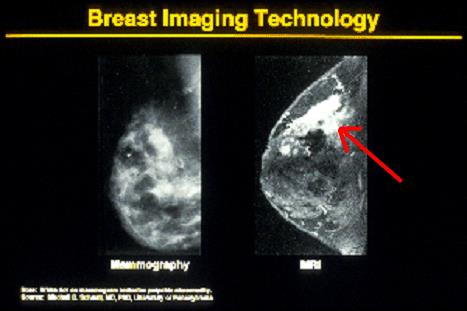
modern cv: medical imaging
state of the art today?
computer vision and nearby fields
- Computer Graphics: Models to Images
- Comp. Photography: Images to Images
- Computer Vision: Images to Models
Derogatory summary of computer vision: Machine learning applied to visual data
sub-domains of computer vision
Sub-domains of computer vision include:
- scene reconstruction
- event detection
- video tracking
- object recognition
- object pose estimation
- learning
- indexing
- motion estimation
- image restoration
- ...
Course details
We will not have time to touch all that computer vision has to offer
Instead, we will focus on understanding the fundamentals of CV through interesting applications and projects
Fundamentals:
- acquisition
- pre-processing
- feature extraction
- detection/segmentation
- high-level processing
- decision making
tentative projects
- Image filtering and hybrid images
- Local feature matching
- Estimating fundamental matrices
- Object detection with a Sliding Window
- Scene recognition with Bag of Words
- Boundary Detection
Project: Image filtering and hybrid images
Implement image filtering to separate high and low frequencies
Combine high frequencies and low frequencies from different images to create an image with scale-dependent interpretation

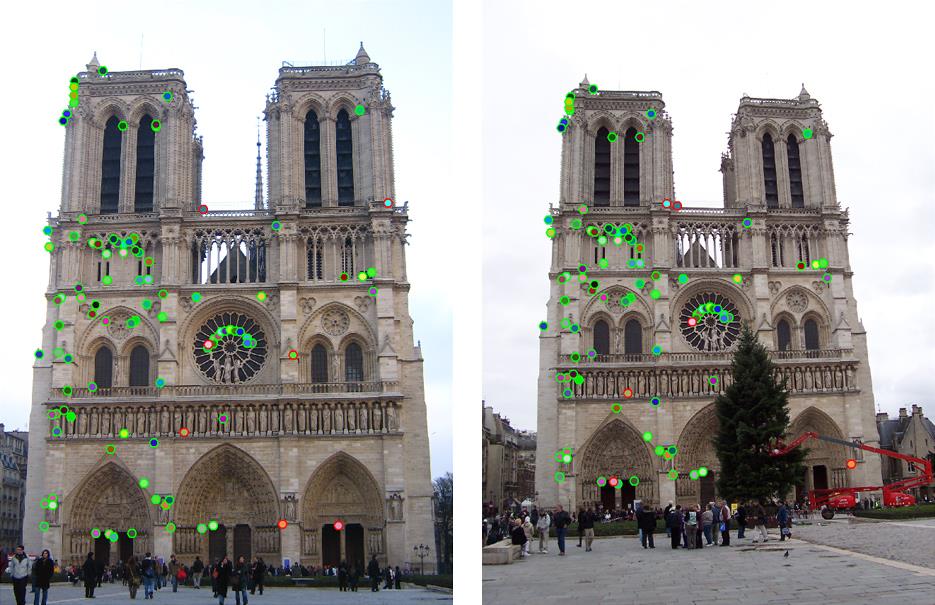
project: local feature matching
Implement interest point detector, SIFT-like local feature descriptor, and simple matching algorithm

project: estimating fundamental matrices
a.k.a., camera motion reconstruction
Locate and track features through a pair of images or a short video to reconstruct the camera's motion
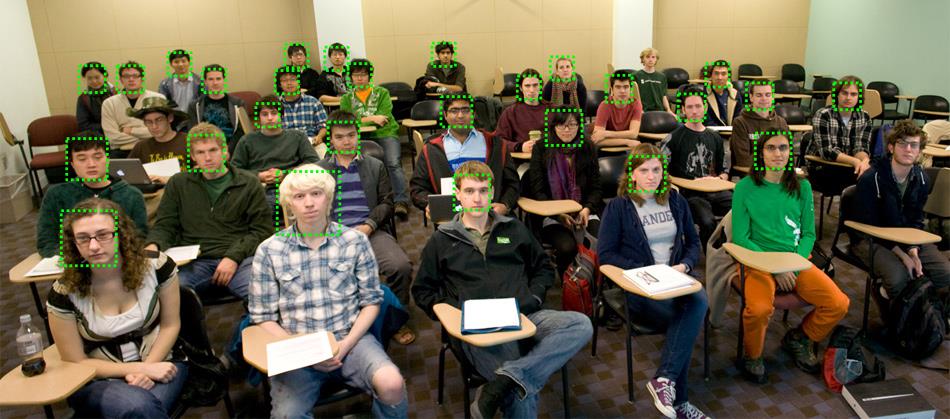
project: object detection with sliding window
Train a face detector based on positive examples and "mined" hard negatives, detect faces at multiple scales and suppress duplicate detections

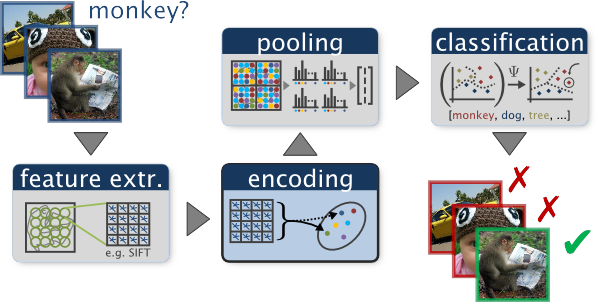
project: scene recognition with bag of words
Quantize local features into a "vocabulary", describing images as histograms of "visual words", train classifiers to recognize scenes based on these histograms
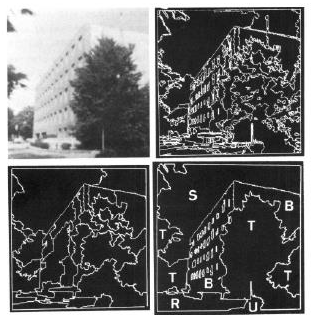
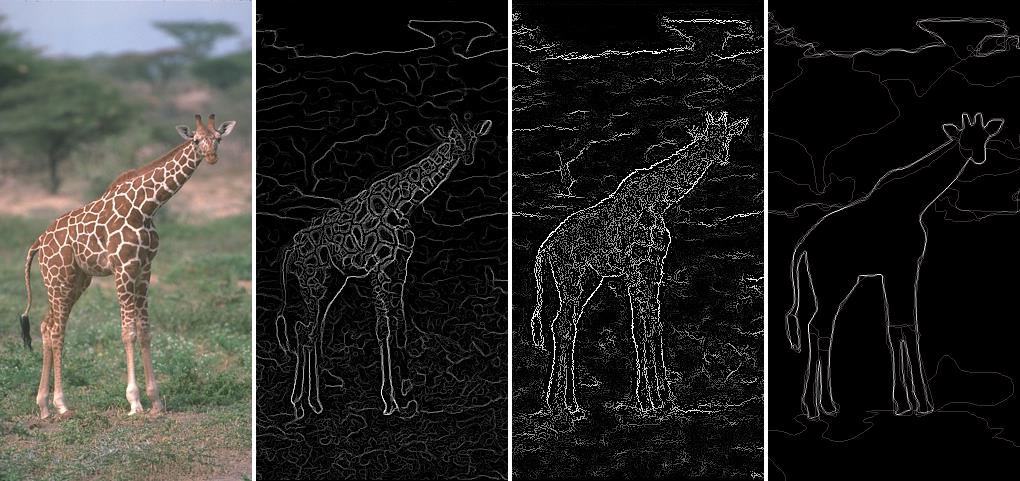
project: boundary detection
Quantize human-annotated boundaries into "sketch tokens", train a multi-way classifier to recognize such tokens
other assignments
Reading, understanding, presenting CV research papers
Group application project
- Photo booth with digital props
- Kinect game
- Sudoku solver
- ...?
