Lights and Materials
COS 350 - Computer Graphics
Lighting the scene
Lighting the scene
Naïve approach is to assign to each vertex a color that seems as though it is lit.
Does not work if we transform the light, the object, or the camera!
Model lights and materials
definition (non-technical)
- Materials
- the surface characteristics that describe how the light is reflected, absorbed, transmitted, scattered, emitted, etc., off/at the surface.
light model
Light properties:
light model
Light properties:
- position
- orientation
- color + brightness
- type (point, spot, directional, etc.)
- properties of type
material model
Material properties:
material model
Material properties:
- color (diffuseness)
- shininess (reflectiveness/specularity)
- translucency (transmittance)
- subsurface scattering
- emittance
geometry model
Geometry properties:
geometry model
Geometry properties:
- position
- orientation (normal, tangents)
simplified model
For now, we will only consider a small subset of these properties:
- Light (directional)
- orientation
- color + brightness
- type: directional
- Material
- diffuse color
- Geometry
- normal
simplified model
simplified light
Directional light has no position, only an orientation.
Define this as a direction (unit vector)
Specified in shader using uniform vec3, because the direction will not change for each fragment.
simplified light
Similarly, the color and brightness can be specified in shader as uniform vec3.
simplified material + geometry
The intensity of light that is reflected into the camera by the material of the surface depends on:
- the reflectiveness of the material
- the orientation of the surface relative to the light's orientation
simplified material + geometry
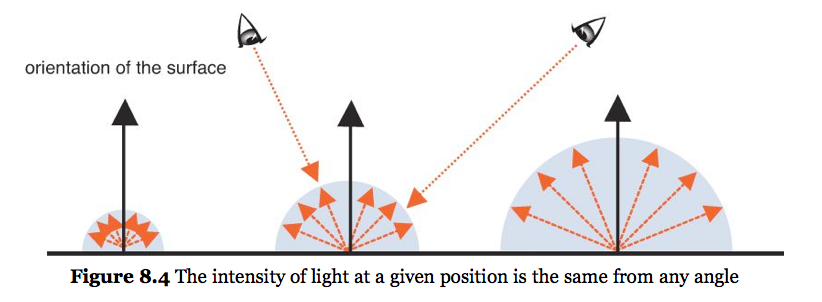
Diffuse materials scatter incident light equally in all directions, independent of the camera's orientation to the surface. (e.g., moon)
simplified material + geometry
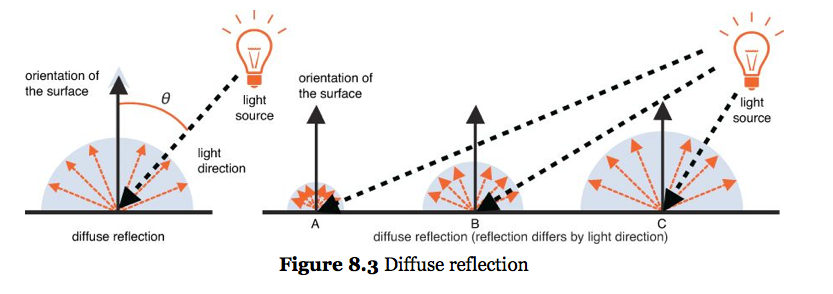
The intensity of reflected light does depend on the relative orientation of the surface to the light source. In other words, as the surface "turns away" from the light, the intensity of reflected light falls off.
simplified material + geometry

This fall-off can be computed as \(\cos(\theta)\), the cosine of the angle between the surface normal (\(\n\)) and the lighting direction (\(\l\)). Another mathematically equivalent way: \(\n \cdot \l\)
definition
- normal
- the direction that points "outside" the surface and is perpendicular to all tangent directions of the surface
lighted cube (animated)
lighted cube (animated)
// LightedCube_animation.js (c) 2012 matsuda
// Vertex shader program
var VSHADER_SOURCE =
'attribute vec4 a_Position;\n' +
'attribute vec4 a_Color;\n' +
'attribute vec4 a_Normal;\n' +
'uniform mat4 u_MvpMatrix;\n' +
'uniform mat4 u_NormalMatrix;\n' +
'uniform vec3 u_LightDirection;\n' +
'varying vec4 v_Color;\n' +
'void main() {\n' +
' gl_Position = u_MvpMatrix * a_Position;\n' +
' vec4 normal = u_NormalMatrix * a_Normal;\n' +
' float nDotL = max(dot(u_LightDirection, normalize(normal.xyz)), 0.0);\n' +
' v_Color = vec4(a_Color.xyz * nDotL, a_Color.a);\n' +
'}\n';
// Fragment shader program
var FSHADER_SOURCE =
'#ifdef GL_ES\n' +
'precision mediump float;\n' +
'#endif\n' +
'varying vec4 v_Color;\n' +
'void main() {\n' +
' gl_FragColor = v_Color;\n' +
'}\n';
function main() {
// Retrieve <canvas> element
var canvas = document.getElementById('webgl');
// Get the rendering context for WebGL
var gl = getWebGLContext(canvas);
if (!gl) {
console.log('Failed to get the rendering context for WebGL');
return;
}
// Initialize shaders
if (!initShaders(gl, VSHADER_SOURCE, FSHADER_SOURCE)) {
console.log('Failed to initialize shaders');
return;
}
//
var n = initVertexBuffers(gl);
if (n < 0) {
console.log('Failed to set the vertex information');
return;
}
// Set the clear color and enable the depth test
gl.clearColor(0, 0, 0, 1);
gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST);
// Get the storage locations of uniform variables and so on
var u_MvpMatrix = gl.getUniformLocation(gl.program, 'u_MvpMatrix');
var u_NormalMatrix = gl.getUniformLocation(gl.program, 'u_NormalMatrix');
var u_LightDirection = gl.getUniformLocation(gl.program, 'u_LightDirection');
if (!u_MvpMatrix || !u_NormalMatrix || !u_LightDirection) {
console.log('Failed to get the storage location');
return;
}
var vpMatrix = new Matrix4(); // View projection matrix
// Calculate the view projection matrix
vpMatrix.setPerspective(30, canvas.width/canvas.height, 1, 100);
vpMatrix.lookAt(3, 3, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0);
// Set the light direction (in the world coordinate)
var lightDirection = new Vector3([0.5, 3.0, 4.0]);
lightDirection.normalize(); // Normalize
gl.uniform3fv(u_LightDirection, lightDirection.elements);
var currentAngle = 0.0; // Current rotation angle
var modelMatrix = new Matrix4(); // Model matrix
var mvpMatrix = new Matrix4(); // Model view projection matrix
var normalMatrix = new Matrix4(); // Transformation matrix for normals
var tick = function() {
currentAngle = animate(currentAngle); // Update the rotation angle
// Calculate the model matrix
modelMatrix.setRotate(currentAngle, 0, 1, 0); // Rotate around the y-axis
mvpMatrix.set(vpMatrix).multiply(modelMatrix);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(u_MvpMatrix, false, mvpMatrix.elements);
// Pass the matrix to transform the normal based on the model matrix to u_NormalMatrix
normalMatrix.setInverseOf(modelMatrix);
normalMatrix.transpose();
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(u_NormalMatrix, false, normalMatrix.elements);
// Clear color and depth buffer
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// Draw the cube
gl.drawElements(gl.TRIANGLES, n, gl.UNSIGNED_BYTE, 0);
requestAnimationFrame(tick, canvas); // Request that the browser ?calls tick
};
tick();
}
function draw(gl, n, angle, vpMatrix, u_MvpMatrix, u_NormalMatrix) {
}
function initVertexBuffers(gl) {
// Create a cube
// v6----- v5
// /| /|
// v1------v0|
// | | | |
// | |v7---|-|v4
// |/ |/
// v2------v3
// Coordinates
var vertices = new Float32Array([
1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0,-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0, 1.0, // v0-v1-v2-v3 front
1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0,-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0, // v0-v3-v4-v5 right
1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,-1.0, -1.0, 1.0, 1.0, // v0-v5-v6-v1 up
-1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0,-1.0, -1.0,-1.0,-1.0, -1.0,-1.0, 1.0, // v1-v6-v7-v2 left
-1.0,-1.0,-1.0, 1.0,-1.0,-1.0, 1.0,-1.0, 1.0, -1.0,-1.0, 1.0, // v7-v4-v3-v2 down
1.0,-1.0,-1.0, -1.0,-1.0,-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0 // v4-v7-v6-v5 back
]);
// Colors
var colors = new Float32Array([
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, // v0-v1-v2-v3 front
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, // v0-v3-v4-v5 right
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, // v0-v5-v6-v1 up
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, // v1-v6-v7-v2 left
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, // v7-v4-v3-v2 down
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0 // v4-v7-v6-v5 back
]);
// Normal
var normals = new Float32Array([
0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, // v0-v1-v2-v3 front
1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, // v0-v3-v4-v5 right
0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, // v0-v5-v6-v1 up
-1.0, 0.0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, // v1-v6-v7-v2 left
0.0,-1.0, 0.0, 0.0,-1.0, 0.0, 0.0,-1.0, 0.0, 0.0,-1.0, 0.0, // v7-v4-v3-v2 down
0.0, 0.0,-1.0, 0.0, 0.0,-1.0, 0.0, 0.0,-1.0, 0.0, 0.0,-1.0 // v4-v7-v6-v5 back
]);
// Indices of the vertices
var indices = new Uint8Array([
0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3, // front
4, 5, 6, 4, 6, 7, // right
8, 9,10, 8,10,11, // up
12,13,14, 12,14,15, // left
16,17,18, 16,18,19, // down
20,21,22, 20,22,23 // back
]);
// Write the vertex property to buffers (coordinates, colors and normals)
if (!initArrayBuffer(gl, 'a_Position', vertices, 3, gl.FLOAT)) return -1;
if (!initArrayBuffer(gl, 'a_Color', colors, 3, gl.FLOAT)) return -1;
if (!initArrayBuffer(gl, 'a_Normal', normals, 3, gl.FLOAT)) return -1;
// Unbind the buffer object
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, null);
// Write the indices to the buffer object
var indexBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
if (!indexBuffer) {
console.log('Failed to create the buffer object');
return false;
}
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
return indices.length;
}
function initArrayBuffer(gl, attribute, data, num, type) {
// Create a buffer object
var buffer = gl.createBuffer();
if (!buffer) {
console.log('Failed to create the buffer object');
return false;
}
// Write date into the buffer object
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, data, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Assign the buffer object to the attribute variable
var a_attribute = gl.getAttribLocation(gl.program, attribute);
if (a_attribute < 0) {
console.log('Failed to get the storage location of ' + attribute);
return false;
}
gl.vertexAttribPointer(a_attribute, num, type, false, 0, 0);
// Enable the assignment of the buffer object to the attribute variable
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_attribute);
return true;
}
// Rotation angle (degrees/second)
var ANGLE_STEP = 30.0;
// Last time that this function was called
var g_last = Date.now();
function animate(angle) {
// Calculate the elapsed time
var now = Date.now();
var elapsed = now - g_last;
g_last = now;
// Update the current rotation angle (adjusted by the elapsed time)
var newAngle = angle + (ANGLE_STEP * elapsed) / 1000.0;
return newAngle %= 360;
}
transforming points, directions, normals
Transforming a point \(\x\) (vector) by the transformation matrix \(M\) is done by simple matrix-vector multiplication
\[M \x\]
Transforming a direction \(\d\) (unit vector) by the transformation matrix \(M\) is done by simple matrix-vector multiplication followed by a normalization (make result unit vector!)
\[\frac{M \d}{||M \d||}\]
transforming points, directions, normals
However, transforming a normal \(\n\) (perpendicular unit vector) by the transformation matrix \(M\) is done by multiplying with the inverse transpose of \(M\) followed by a normalization.
\[\frac{(M^T)^{-1} \n}{||(M^T)^{-1} \n||}\]
Proof:
- By definition: \(\t \cdot \n = \t^T\n = 0\)
- After transform: \((M \t)^T (X \n) = 0\)
- For all \(\t\) we have: \(\t^T M^T X \n = 0\)
- Which gives: \(\t^T M^T (M^T)^{-1} \n = 0\)
- Note: \((M^T)^{-1} = (M^{-1})^T\)
what if normal isn't given?
Surface normal can be computed as normalized cross product of two independent surface tangents
For triangle, choose two edges as tangents.
Gourard shading
Recall that Gourard shading is done by computing the "color" at each vertex of a triangle and interpolating these colors across the surface (varying vec3 v_color).
Phong shading
Phong shading interpolates the normal of each vertex across the triangle and computes the "color" at each fragment (varying vec3 v_normal).
